

RADIATION
SIDE
EFFECTS
Potential Side Effects of Prostate Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy is a standard form of treatment that uses energy beams to destroy cancer cells and stop them from spreading. Per the National Cancer Institute, it is possible for patients receiving radiation therapy for prostate cancer to experience "an acceptably low complication rate, if care is given to the delivery technique."1
During treatment, however, radiation beams may reach healthy tissue reach healthy tissue near the intended treatment area, resulting in radiation side effects.2
Short-term side effects are those that appear during or shortly after radiation treatment and are typically temporary. The type and severity of side effects can vary.3 Talk with your doctor about what to expect and resources for managing any symptoms.
Long-term side effects of radiation therapy for prostate cancer may develop over time and can include urinary, bowel, or sexual complications.3 Talk with your doctor both before and after treatment if you have any concerns.
Reducing Radiation Therapy Rectal Side Effects
Barrigel™ rectal spacer is a hyaluronic gel that's placed between the prostate and rectum before radiation therapy. By creating space between the prostate and the anterior (front) wall of the rectum, it helps limit the amount of high-dose radiation that reaches the rectum during treatment.3
The gel stays in place throughout the course of radiation and is gradually absorbed by the body over time.4,5
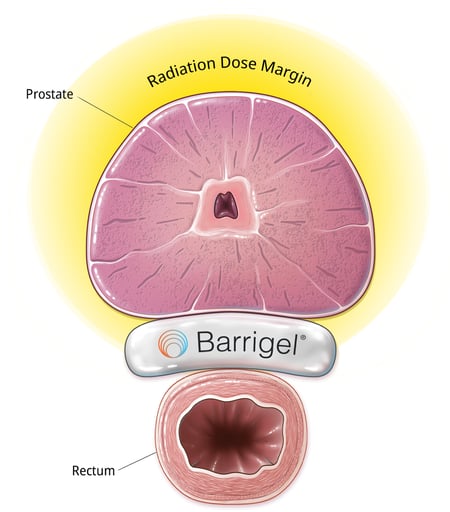
Barrigel™ rectal spacer creates space between the prostate and the rectum, moving the healthy organ out of the high-dose radiation area, reducing radiation exposure to the rectum.
Barrigel™ rectal spacer is a hydrogel that is inserted between the prostate and rectum during treatment. It creates space to reduce radiation exposure to the rectum. Clinical trials have shown that rectal spacers significantly reduce the risk of rectal complications following prostate radiation.4,6,7
Talk to your doctor to see if this approach is right for your treatment plan.
References
- 1. American Cancer Society. Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer. Accessed April 2025. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/prostate-cancer/treating/radiation-therapy.html
2. Cancer Research UK. Long-term Side Effects of External Radiotherapy. Cancer Research UK. Published April 20, 2023. Accessed May 12, 2025. https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/prostate-cancer/treatment/radiotherapy/external-radiotherapy/long-term-side-effects-external-radiotherapy.
3. Mayo Clinic. Radiation Therapy. www.mayoclinic.org. Accessed: April 29, 2025. https://www.Mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/radiation-therapy/about/pac-20385162
4. Mariados NF, Orio PF III, King M et al. JAMA Oncol (2023)* https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18313526
5. OncoLink. Possible Side Effects of Radiation Treatment for Prostate Cancer. Abramson Cancer Center, University of Pennsylvania. Apr 2025. https://www.oncolink.org/cancers/prostate/treatments/possible-side-effects-of-radiation-treatment-for-prostate-cancer
6. Mariados N, Sylvester J, Shah D et al. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys (2015).
7. Song D et al, Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys (2024)
*Study sponsored by Palette Life Sciences, now part of Teleflex
